PhytoVero - organic cosmetics philosophy skin facts
skin facts
The skin is the largest and most delicate organ of our body. Every skin has different requirements and characteristics. Whether normal skin, dry skin or mature skin: every skin type has its own care needs.
PhytoVero develops both light body lotions and rich body creams, which have moisturizing properties and offer the skin a plus in care. There are also different needs when it comes to body cleansing. We try to meet all wishes, but always pay attention to our motto: What comes on the skin must be food safe, biocide-free, sustainably cultivated and fair-trade!
About our skin:
Our skin has many different functions. It serves as a protective barrier against external influences, is important for homeostasis (self-regulation) and plays a role in sensory perception and communication. It can be divided into three layers: the epidermis, the dermis (cutis) and the subcutis. The epidermis is covered by a thin film of fluid. This has a pH value of 4.2-5.6. Therefore 'skin-neutral' does not mean pH 7.0. The liquid film is important to ward off microorganisms. It is therefore important to ensure that no alkaline cosmetics are used. Often we find in deodorants sodium bicarbonate or sodium hydroxide which change the skin flora lastingly.
The epidermis can be divided into five areas: the stratum corneum, which consists of dead cells, the stratum lucidum, the stratum granulosum, the stratum spinosum and the stratum basale. The epidermis is an effective barrier against penetration of substances. The skin layers show different polarities and different water contents. The stratum corneum, for example, is largely low in water and lipophilic. Between the dead cells (intercellular spaces) there are skin lipids which are
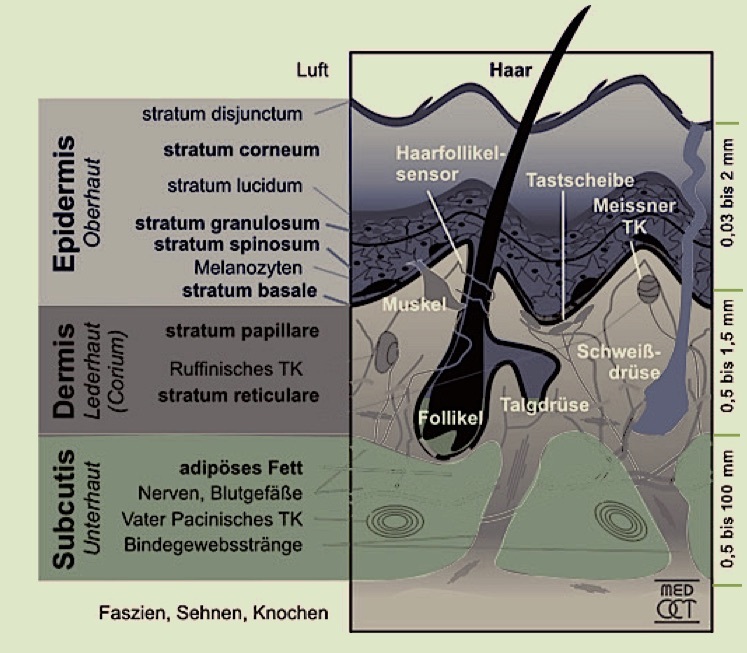
in a relatively rigid state (ceramides, fatty acids, cholesterol (cholesterol) and cholesterol derivatives, but no phospholipids). The movement of molecules in and through such areas is difficult. The lipophilic areas of the upper epidermis are followed by hydrophilic areas. The dermis contains the blood vessels, sebaceous glands and sweat glands. The subcutis consists primarily of fatty tissue.
Several routes are possible to penetrate the skin. The substance can penetrate through the cells. One speaks of the transcellular route. The passage through the intercellular space is called the intercellular route. The uptake by the hair follicles (transfollicular) and the glandular channels (transglandular) plays a subordinate role in the uptake of substances. Only a few substances can penetrate the barrier and invade the deeper skin layers. Factors influencing the absorption of a substance into the skin are the proportion of lipophilic and hydrophilic molecule regions, the size of the molecule, the dissociability of the molecule and the concentration of the substance on the skin.